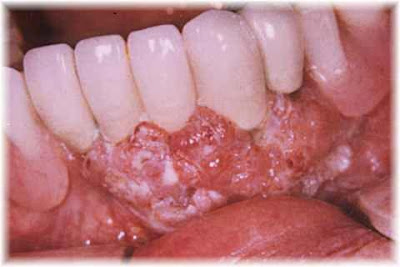
Hey at least it slightly cleaner than the rest.
Thursday, July 31, 2008
Tuesday, July 22, 2008
Saturday, July 19, 2008
It's time to quit!
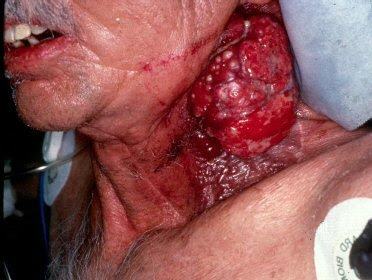
Friday, July 18, 2008
Thursday, July 17, 2008
Wednesday, July 16, 2008
Tuesday, July 15, 2008
Monday, July 14, 2008
Anti-Smoking Commercials
I remember seeing this commercial when I was a kid. Not as effective as it should have been.
Sunday, July 13, 2008
What is Lung Cancer?
From Wikipedia: Lung cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. This growth may lead to metastasis, invasion of adjacent tissue and infiltration beyond the lungs. The vast majority of primary lung cancers are carcinomas of the lung, derived from epithelial cells. Lung cancer, the most common cause of cancer-related death in men and the second most common in women,[1][2] is responsible for 1.3 million deaths worldwide annually.[3] In the UK, it is the most common site of fatal cancer in both men and women. The most common symptoms are shortness of breath, coughing (including coughing up blood), and weight loss.[4]
The main types of lung cancer are small cell lung carcinoma and non-small cell lung carcinoma. This distinction is important because the treatment varies; non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is sometimes treated with surgery, while small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) usually responds better to chemotherapy and radiation.[5] The most common cause of lung cancer is long term exposure to tobacco smoke.[6] The occurrence of lung cancer in non-smokers, who account for as many as 20% of cases, often attributed to a combination of genetic factors,[7][8] radon gas,[9] asbestos,[10] and air pollution,[11][12][13] including second-hand smoke.[14][15]
Saturday, July 12, 2008
Not just cancer but tumors too!
Friday, July 11, 2008
What is Lung Cancer?
Cancer of the lung, like all cancers, results from an abnormality in the body's basic unit of life, the cell. Normally, the body maintains a system of checks and balances on cell growth so that cells divide to produce new cells only when needed. Disruption of this system of checks and balances on cell growth results in an uncontrolled division and proliferation of cells that eventually forms a mass known as a tumor.
Tumors can be benign or malignant; when we speak of "cancer," we refer to those tumors that are considered malignant. Benign tumors can usually be removed and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, grow aggressively and invade other tissues of the body, allowing entry of tumor cells into the bloodstream or lymphatic system which spread the tumor to other sites in the body. This process of spread is termed metastasis; the areas of tumor growth at these distant sites are called metastases. Since lung cancer tends to spread, or metastasize, very early in its course, it is a very life-threatening cancer and one of the most difficult cancers to treat. While lung cancer can spread to any organ in the body, certain organs—particularly the adrenal glands, liver, brain, and bone—are the most common sites for lung cancer metastasis.
The lung is also a very common site for metastasis from tumors in other parts of the body. Tumor metastases are made up of the same type of cells as the original, or primary, tumor. For example, if prostate cancer spreads via the bloodstream to the lungs, it is metastatic prostate cancer in the lung and is not lung cancer.